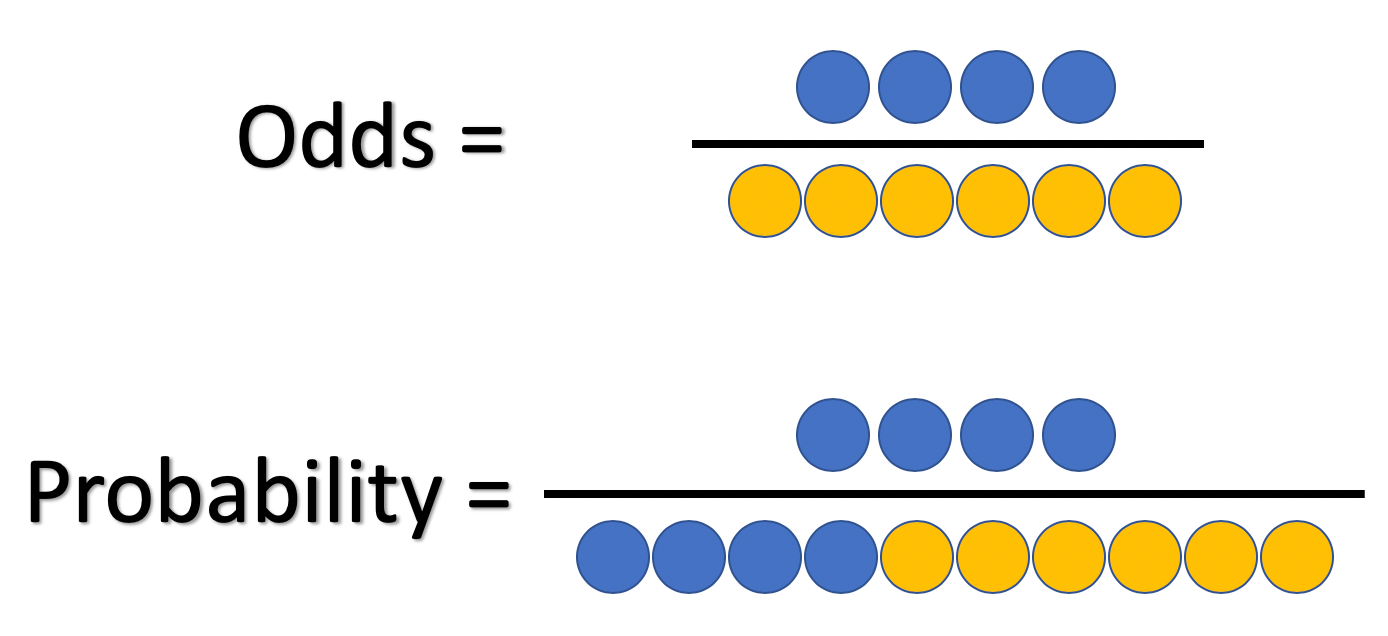
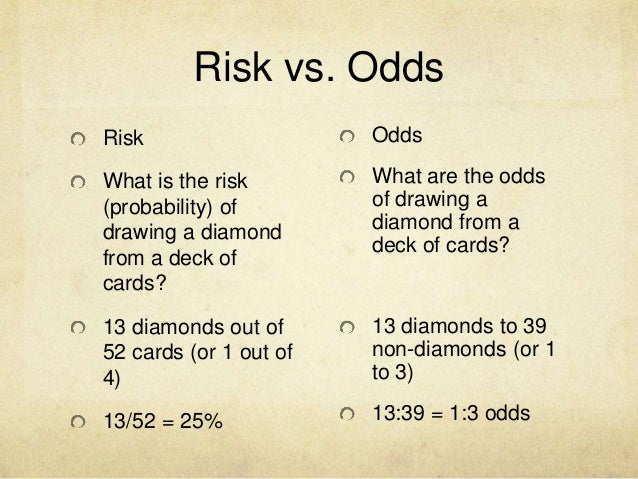
Feb 19, 18 · The primary difference between odds and probability is that while odds is a ratio of occurrence to nonoccurrence, the probability is the ratio of occurrence to the whole Odds are expressed in the ratio, the probability is either written in percentage form or in decimalAbout Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us CreatorsJul 11, 16 · The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk is also called the risk ratio) Let's look at an example Relative Risk/Risk Ratio Suppose you have a school that wants to test out a new tutoring program
3 5 Bias Confounding And Effect Modification Stat 507
Odds versus relative risk
Odds versus relative risk-Sometimes, we see the log odds ratio instead of the odds ratio The log OR comparing women to men is log(144) = 036 The log OR comparing men to women is log(069) = 036 log OR > 0 increased risk log OR = 0 no difference in risk log OR < 0 decreased risk Odds Ratio 0 5 10 15 More on the Odds Ratio Log Odds Ratio4 2 0 2 4Dec 14, 14 · The relative risk of losing weight by choosing diet A over diet B is 1125, while the odds ratio is about 225 The reasons a medical article might choose one method of reporting over the other are complex, but the message here is that sorting that out starts by being clear about the difference between probability and odds




Odds Ratio Wikipedia
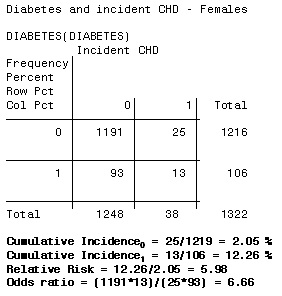
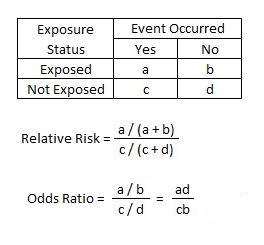
Apr 21, 21 · Comparing AstraZeneca vaccine bloodclot risk to odds of dying in a car crash unhelpful, experts say Downplaying the risk with inappropriate comparisons will not build coronavirus vaccineThe relative risk and the odds ratio are measures of association between exposure status and disease outcome in a population Relative risk In epidemiology, relative risk (RR) can give us insights in how much more likely an exposed group is to develop a certain disease in comparison to a nonexposed group Once we know the exposure and disease status of a research population,Rather the odds is threefold greater Interpretation of an OR must be in terms of odds, not
Lifetime odds of death for selected causes, United States, 19;Cause of Death Odds of Dying;Apr 21, 21 · Risk Difference = CI e CI u = 090 058 = 032 = 32 per 100 Interpretation Among smokers there were 32 excess cases of respiratory disease per 100 smokers during the 18 year study It is also possible for a risk ratio to be
Jan 08, 16 · Percent decrease = (1 – Risk Ratio upper bound) x 100 It's worth stating again when comparing two proportions close to 1 or 0, the risk ratio is usually a better summary than the raw difference Odds Ratios We now turn to odds ratios as yet another way to summarize a 2 x 2 table Odds are another way of expressing the likelihood ofOct 12, 15 · The odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of odds of an event in one group versus the odds of the event in the other group An RR (or OR) of 10 indicates that there is no difference in risk (or odds) between the groups being comparedFeb 17, 21 · For example, a relative risk of 15 would suggest a 50% increase in risk, whereas a relative risk of 05 would suggest a 50% decrease in risk Odds ratios The main difference between this and the other two measures is that there is no way of including a time element in this model




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




3 5 Bias Confounding And Effect Modification Stat 507
The odds differ from the risk, and while the odds may appear to be high, the absolute risk may be low Handling continuous input variables For continuous data (eg, age, height, or weight), it is tempting to divide the subjects into categories (eg, age >50 years vs age ≤50 years)Odds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR)The relative risk (also known as risk ratio RR) is the ratio of risk of an event in one group (eg, exposed group) versus the risk of the event in the other group (eg, nonexposed group) The odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of odds of an event in one group versus the odds




Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio And 95 Confidence Intervals For Download Scientific Diagram




Moving Beyond Odds Ratios Estimating And Presenting Absolute
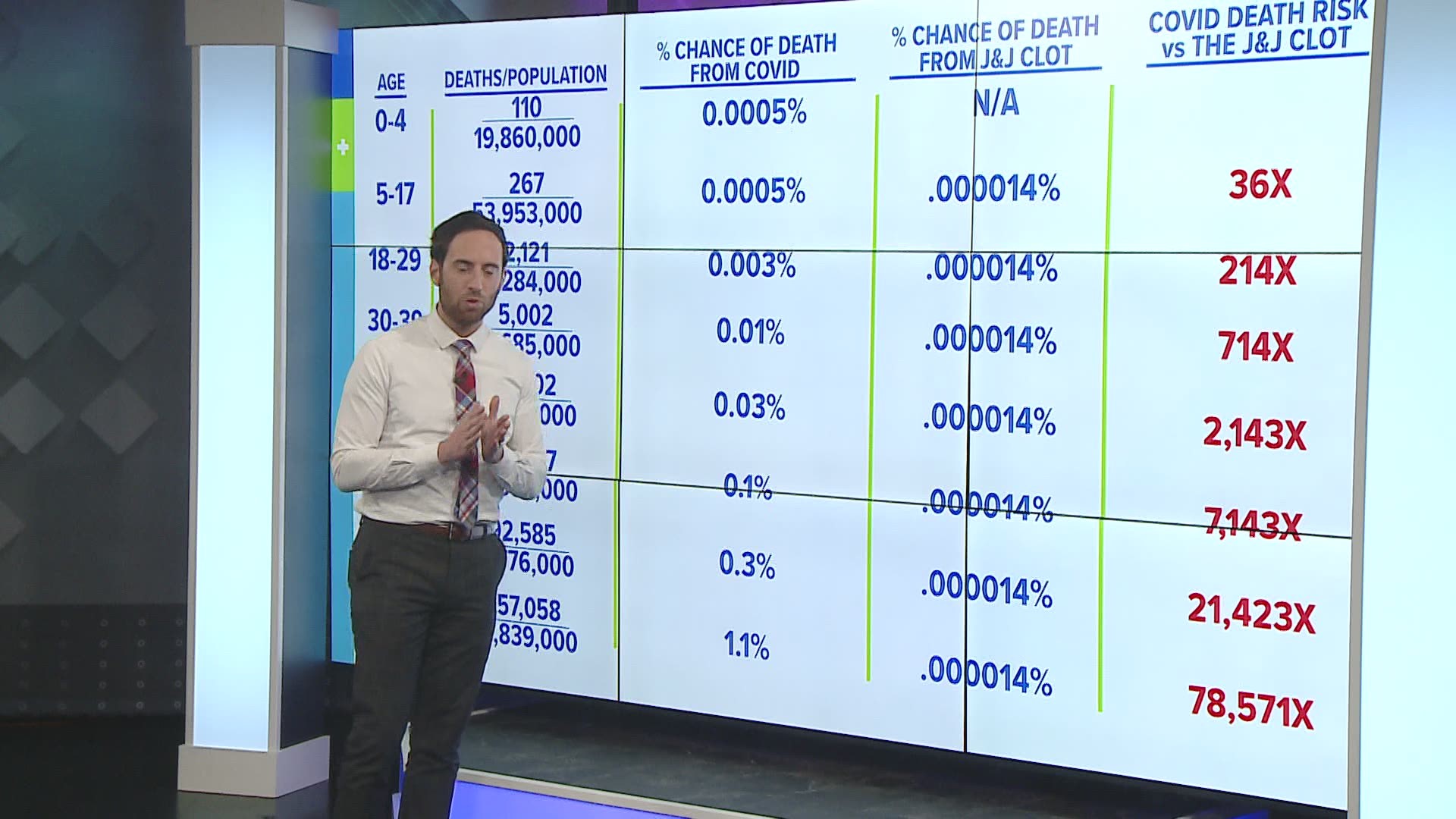
Oct 27, 17 · We are 95% confident that the true odds ratio is between 185 and 2394 The null value is 1, and because this confidence interval does not include 1, the result indicates a statistically significant difference in the odds of breast cancer women with versus low DDT exposure Note that an odds ratio is a good estimate of the risk ratio when the outcome occurs relatively infrequently (The more common the disease, the larger is the gap between odds ratio and relative risk In our example above, p wine and p no_wine were 0009 and 0012 respectively, so the odds ratio was a good approximation of the relative risk OR = 0752 and RR = 075 If the risks were 08 and 09, the odds ratio and relative risk will be 2 very different numbers OR = 044 and RR = 0 Relative risk vs OddsStatistically speaking, the only way to compare this fairly is to compare the risk of contracting COVID19 and then dying from COVID19 to the risk presented from the J&J vaccine as we currently know it




Lecture3




Image Result For Odds Ratio And Risk Ratio And Cohort Study And Case Study
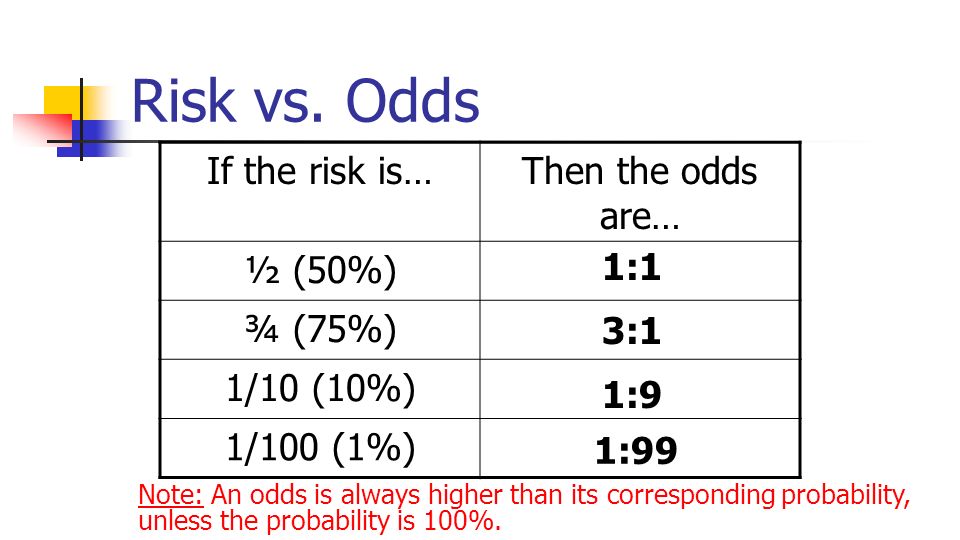
Jun 10, 18 · It is usually expressed as a ratio of two integers For example an odds of 01 is written as 110 and an odds of 5 is written as 51 Risk and risk ratios are more commonly used than odds and odds ratios in medicine as these are much more intuitive Risk describes the probability of an event occurringMay 04, 09 · A crude odds ratio can be converted to a crude risk ratio risk ratio = odds ratio/(1 − p0) (p0 × odds ratio), in which p0 is the outcome prevalence (risk) among the unexposed Some have applied this formula to an adjusted odds ratio to obtain an adjusted risk ratio 49 This method can produce biased risk ratios and incorrect confidenceThe difference between odds and risk is small when the event is rare (as illustrated in the first example above where a risk of 0091 was seen to be similar to an odds of 01) When events are common, as is often the case in clinical trials, the differences between odds and risks are large



Stats Guidelines For Logistic Regression Models September 27 1999




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
Feb 07, 14 · When the outcome is not rare in the population, if the odds ratio is used to estimate the relative risk it will overstate the effect of the treatment on the outcome measure The odds ratio will be greater than the relative risk if the relative risk is greater than one and less than the relative riskJan 21, 03 · Calculation of probability (risk) vs odds In statistics, odds are an expression of relative probabilities, generally quoted as the odds in favor The odds (in favor) of an event or a proposition is the ratio of the probability that the event willIn clinical studies, as well as in some other settings, the parameter of greatest interest is often the relative risk rather than the odds ratio The relative risk is best estimated using a population sample, but if the rare disease assumption holds, the odds ratio is a good approximation to the relative risk — the odds is p / (1 − p), so when p moves towards zero, 1 − p moves towards 1




What Are The Odds Of Dying From Covid 19 Vs Lightning Wqad Com



Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios
Risk factor for the disease • Less than 10 indicates that the odds of exposure among casepatients are lower than the odds of exposure among controls The exposure might be a protective factor against the disease The magnitude of the odds ratio is called the "strength of the association" The further away an odds ratio isIn biomedical research, we are often interested in quantifying the relationship between an exposure and an outcome "Odds" and "Risk" are the most common terms which are used as measures of association between variables In this article, which is the fourth in the series of common pitfalls in statistical analysis, we explain the meaning of risk and odds and the difference between the twoDec 30, 16 · INTRODUCTION Odds ratio (OR) and risk ratio (RR) are two commonly used measures of association reported in research studies In crosssectional studies, the odds ratio is also referred to as the prevalence odds ratio (POR) when prevalent cases are included, and, instead of the RR, the prevalence ratio (PR) is calculated




Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Risk Difference Statistics Tutorial 30 Marinstatslectures Youtube
2) Relative Risk and Odds Ratio for the nonobese Relative Risk and Odds Ratio for the obese 3) Overall, you can see that decreasing the baseline incidence will decrease the odds ratio (300 in those who are nonobese versus 129 in those who are obese) Obviously, these results run counterDec 08, 18 · Risk Ratio vs Odds Ratio Whereas RR can be interpreted in a straightforward way, OR can not A RR of 3 means the risk of an outcome is increased threefold A RR of 05 means the risk is cut in half But an OR of 3 doesn't mean the risk is threefold;Aug 07, 14 · Odds ratio vs risk ratio You know the difference between risk and odds A risk is the proportion of subjects with an event in a total group of susceptible subjects Thus, we can calculate the risk of having a heart attack among smokers (infarcted smokers divided by the total number of smokers) and among nonsmokers (the same, but with nonsmokers)




R Calculate And Interpret Odds Ratio In Logistic Regression Stack Overflow



Odds Vs Risk Vantage Research
An RR (or OR) more than 10 indicates an increase in risk (or odds) among the exposed compared to the unexposed, whereas a RR (or OR)The odds ratio ((a/c)/(b/d)) looks at the likelihood of an outcome in relation to a characteristic factor In epidemiological terms, the odds ratio is used as a point estimate of the relative risk in retrospective studies Odds ratio is the key statistic for most casecontrol studiesFeb 03, 14 · The difference between odds ratio and risk ratio While Risk Ratio is the probability of one thing divided by the probability of another (usually in a separated group), Odds Ratio is the odds of one event happening divided by the odds of another



Plos One Different Depths Of Sedation Versus Risk Of Delirium In Adult Mechanically Ventilated Patients A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis




Odds Ratio Wikipedia
Sep 02, · The risk or odds ratio is the risk or odds in the exposed group divided by the risk or odds in the control group A risk or odds ratio = 1 indicates no difference between the groups A risk or odds ratio > 1 indicates a heightened probability of the outcome in the treatment group The two metrics track each other, but are not equalHeart disease 1 in 6 Cancer 1 in 7 All preventable causes of death 1 in 24 Chronic lower respiratory disease 1 in 27 Suicide 1 in Opioid overdose 1 in 92 Fall 1 in 106 Motorvehicle crash 1 in 107 Gun assault 1 in 2 Pedestrian incident 1 in 543 Motorcyclist 1 in 9 DrowningJan 10, 13 · Odds ratio vs relative risk Odds ratios and relative risks are interpreted in much the same way and if and are much less than and then the odds ratio will be almost the same as the relative risk In some sense the relative risk is a more intuitive measure of effect size




How To Calculate An Odds Ratio Youtube




How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube
Aug 26, · For instance, odds are a symmetric measure, meaning that while risk only examines outcomes given interventions, odds can also examine interventions given outcomes Thus, a study can be constructed where, rather than choosing trial groups and measuring outcomes, outcomes can be chosen, and other factors can be analyzedMay 18, 12 · Attack Rate (Risk) Attack rate for exposed = a ⁄ ab Attack rate for unexposed = c ⁄ cd For this example Risk of tuberculosis among East wing residents = 28 ⁄ 157 = 0178 = 178% Risk of tuberculosis among West wing residents = 4 ⁄ 137 = 0029 = 29% The risk ratio is simply the ratio of these two risks Risk ratio = 178 ⁄ 29 = 61May 15, 14 · The difference between odds ratio and risk ratio May 15, 14 • ericminikel The other day I was emailing with a statistical genetics colleague about a rare SNP associated with a phenotype I stated that the minor allele frequency (MAF) was 07% in cases and 01% in controls, for a risk ratio of 7 After clicking send, I felt a twinge of regret




Numerators Denominators And Populations At Risk Health Knowledge




Ppt The Odds Ratio Relative Odds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6056
Odds Ratio versus Relative Risk Since it is a ratio of ratios, the odds ratio is very difficult to interpret The relative risk is easier to interpret, so the odds ratio alone is not very helpful However, there are certain commonly occurring situations in which the estimate of the relative risk is not very good, and the odds ratio can be usedMar 28, 1998 · Odds ratios are a common measure of the size of an effect and may be reported in casecontrol studies, cohort studies, or clinical trials Increasingly, they are also used to report the findings from systematic reviews and metaanalyses Odds ratios are hard to comprehend directly and are usually interpreted as being equivalent to the relative risk Unfortunately, there is aWe see that the 'relative risk' is now different, but the odds ratio does not change if we change the ratio of cases versus controls Until now we have learned the following 1 we can calculate relative risk IF we can estimate probabilities of an outcome in EACH group 2




Odds Ratio Wikipedia



Summarising Binary Data Health Knowledge
Apr 13, 21 · But what are the odds of dying from a J&J vaccinerelated blood clot versus COVID19 itself, based on your age?• The risk of sexual dysfunction with venlafaxine is 24 times that with placebo • The risk of sexual dysfunction with venlafaxine is 240% that with placebo • Venlafaxine is associated with a 14fold increase in the risk of sexual dysfunction • Venlafaxine is associated with a 140% increase in the risk of sexual dysfunction




The Headline In An Article In The Sacramento Bee R Chegg Com



Ctspedia Ctspedia Oddsrisk




The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor



The Difference Between Probability And Odds




Moving Beyond Odds Ratios Estimating And Presenting Absolute




Odds Ratio Relative Risk By Susi Delaney




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Calculation Definition Probability Odds Youtube




Odds Ratio Article
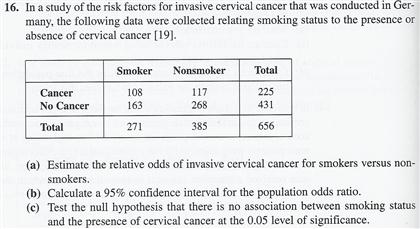



Solved In A Study Of The Risk Factors For Invasive Cervic Chegg Com



Pdf Common Pitfalls In Statistical Analysis Odds Versus Risk




Solved Select All Of The True Statements Regarding The Od Chegg Com




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence
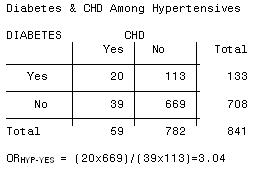



3 5 Bias Confounding And Effect Modification Stat 507
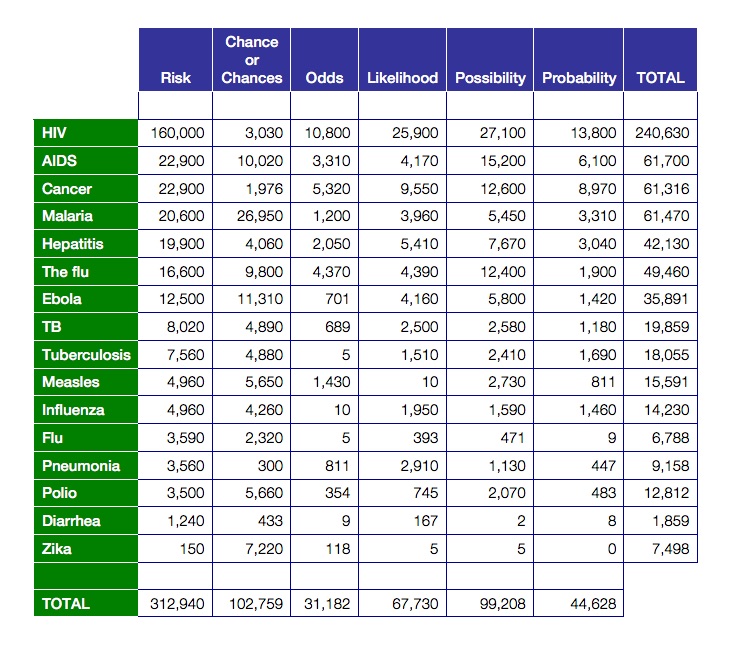



Risk Versus Chance What Are The Odds Health And Communications




Odds Ratio Wikipedia




View Image




Pdf Relative Risks Versus Odds Ratios




Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk




Based On This Chart The Top Of This Question Is P Chegg Com




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal
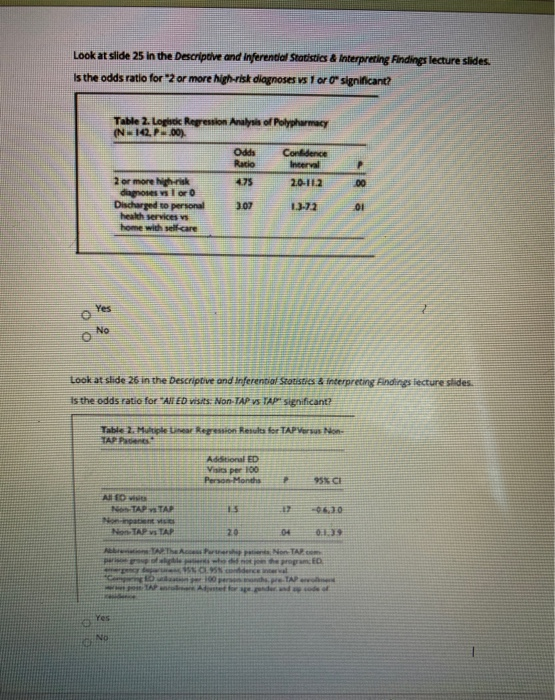



Look At Slide 25 In The Descriptive And Inferentia Chegg Com



Odds Vs Risk Vantage Research




Relation Between The Odds Ratio Relative Risk And Baseline Risk




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube
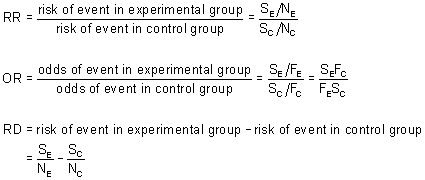



Box 9 2 A Calculation Of Rr Or And Rd
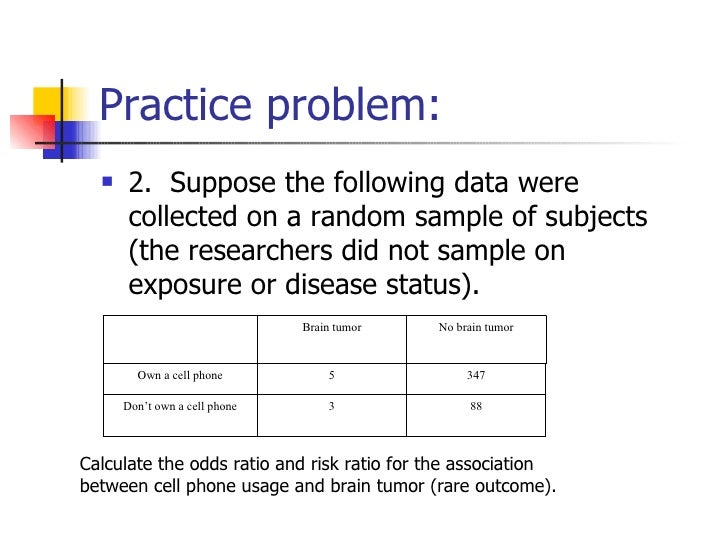



Lecture3




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal




Risks Of And Risk Factors For Covid 19 Disease In People With Diabetes A Cohort Study Of The Total Population Of Scotland The Lancet Diabetes Endocrinology
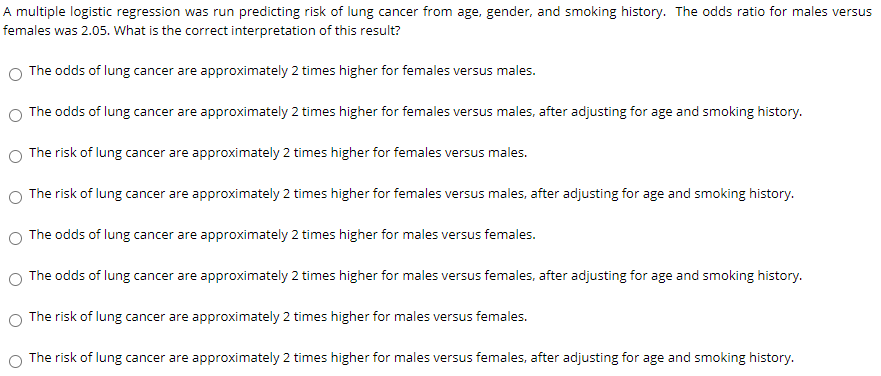



Solved A Multiple Logistic Regression Was Run Predicting Chegg Com




Odds Ratio Relative Risk




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Risk Of In Hospital Morbidity Mortality In Log Odds Versus Vitamin D Download Scientific Diagram
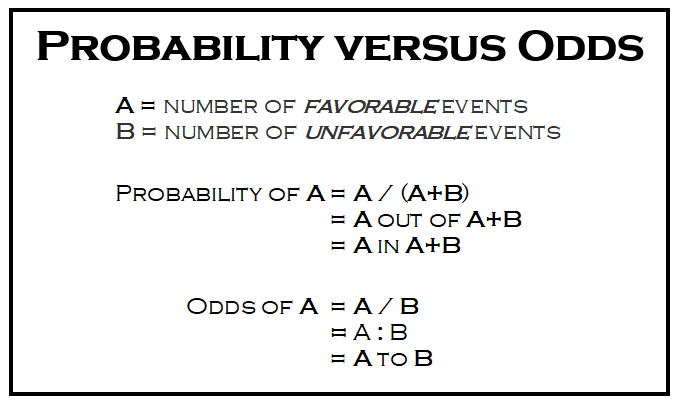



What Are The Odds Stats With Cats Blog




How Much Normal Risk Does Covid Represent By David Spiegelhalter Wintoncentre Medium
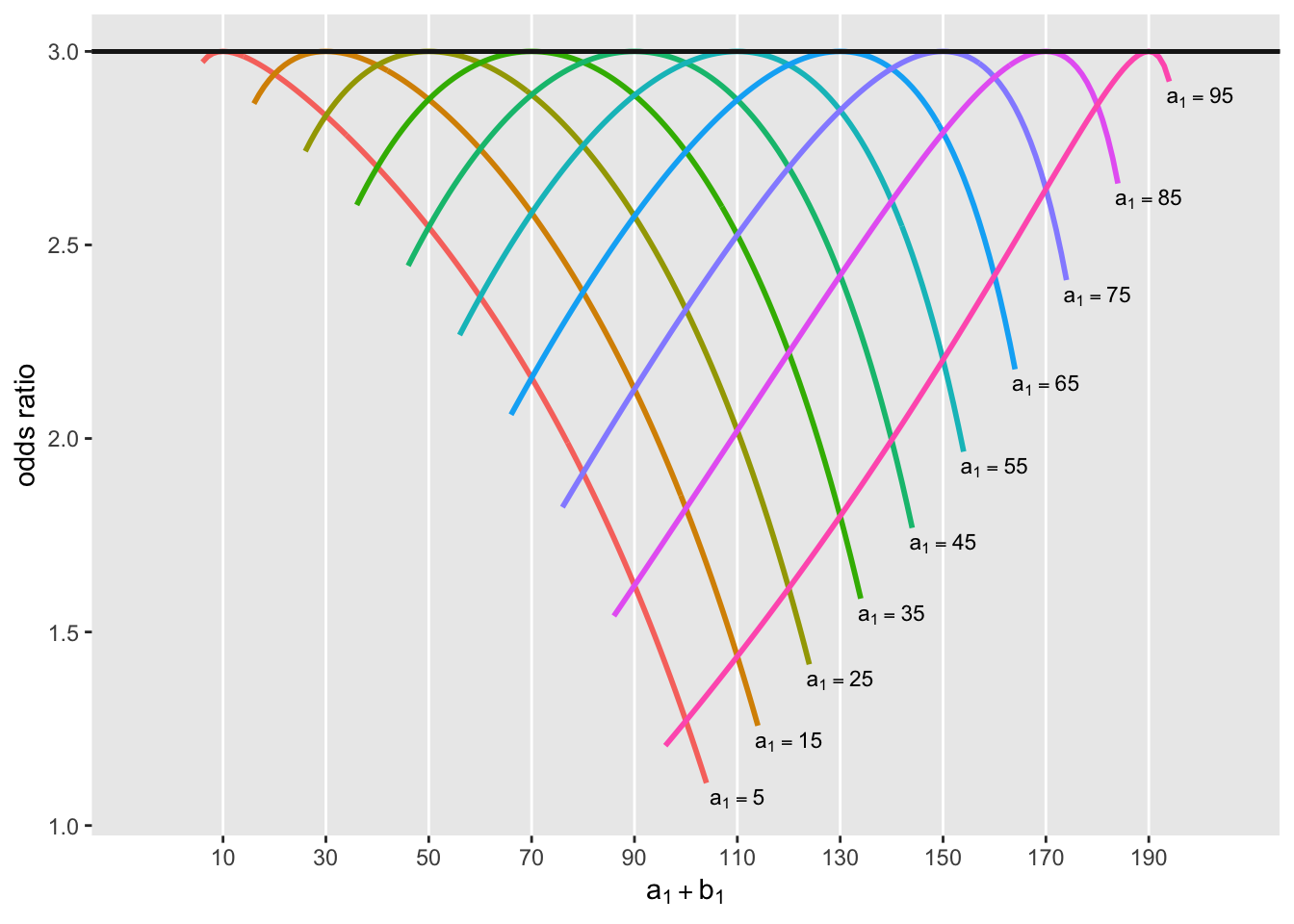



How The Odds Ratio Confounds A Brief Study In A Few Colorful Figures Our Data Generation




Statistics In Medicine Ppt Download




Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk




Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine




Common Measures Of Association In Medical Research Handout



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Measures Of Disease Association Ppt Download




Odds Ratio Calculation And Interpretation Statistics How To




Believability Of Relative Risks And Odds Ratios In Abstracts Cross Sectional Study The Bmj



The Odds Of Dying From A J J Vaccine Related Blood Clot Vs Dying From Covid 19 Newscentermaine Com



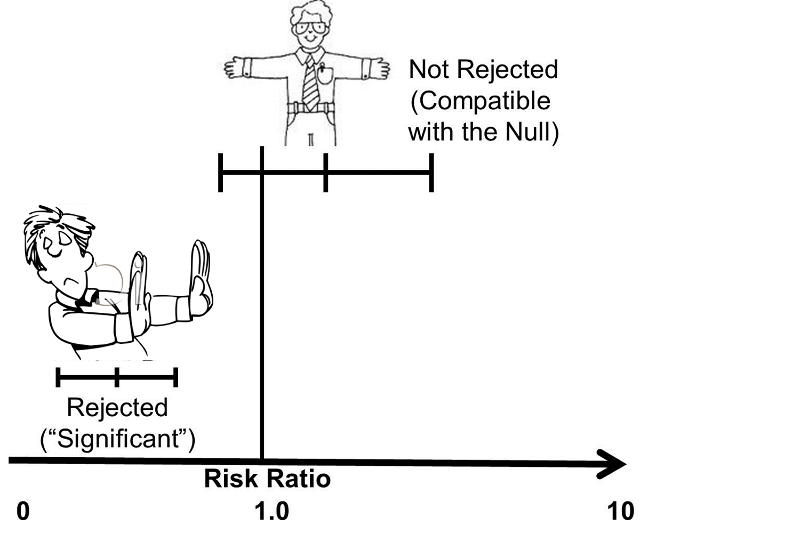
12 13 14 15 16 17 18 Review Sample Size For Surveys Testing Odds Ratio The Odds Ratio And The Relative Risk Are Normally Tested Versus Unity It Is Not Sufficient For The Confidence Interval Not To Cover One But We Must Test With A Given Power That It Is




Relative Risk And Absolute Risk Definition And Examples Statistics How To



What And Why Of Log Odds What Are Log Odds And Why Are They By Piyush Agarwal Towards Data Science



Relative Risk Article




Measures Of Disease Association Measuring Occurrence Of New Outcome Events Can Be An Aim By Itself But Usually We Want To Look At The Relationship Between Ppt Download



Statistics In Medicine Ppt Download




Common Pitfalls In Statistical Analysis Odds Versus Risk Abstract Europe Pmc




Odds Ratio Relative Risk



Plos One Different Depths Of Sedation Versus Risk Of Delirium In Adult Mechanically Ventilated Patients A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis
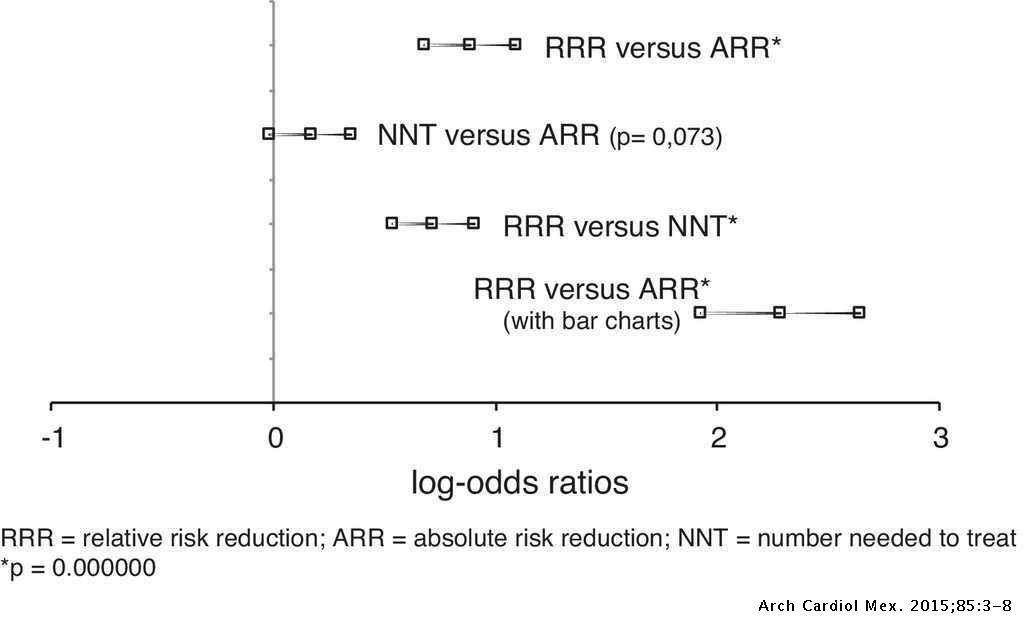



Effects Of Presenting Risk Information In Different Formats To Cardiologists A Latin American Survey Archivos De Cardiologia De Mexico




Risk Versus Chance What Are The Odds Health And Communications



Odds Vs Risk Vantage Research




Retrospective Cohort Study Wikipedia
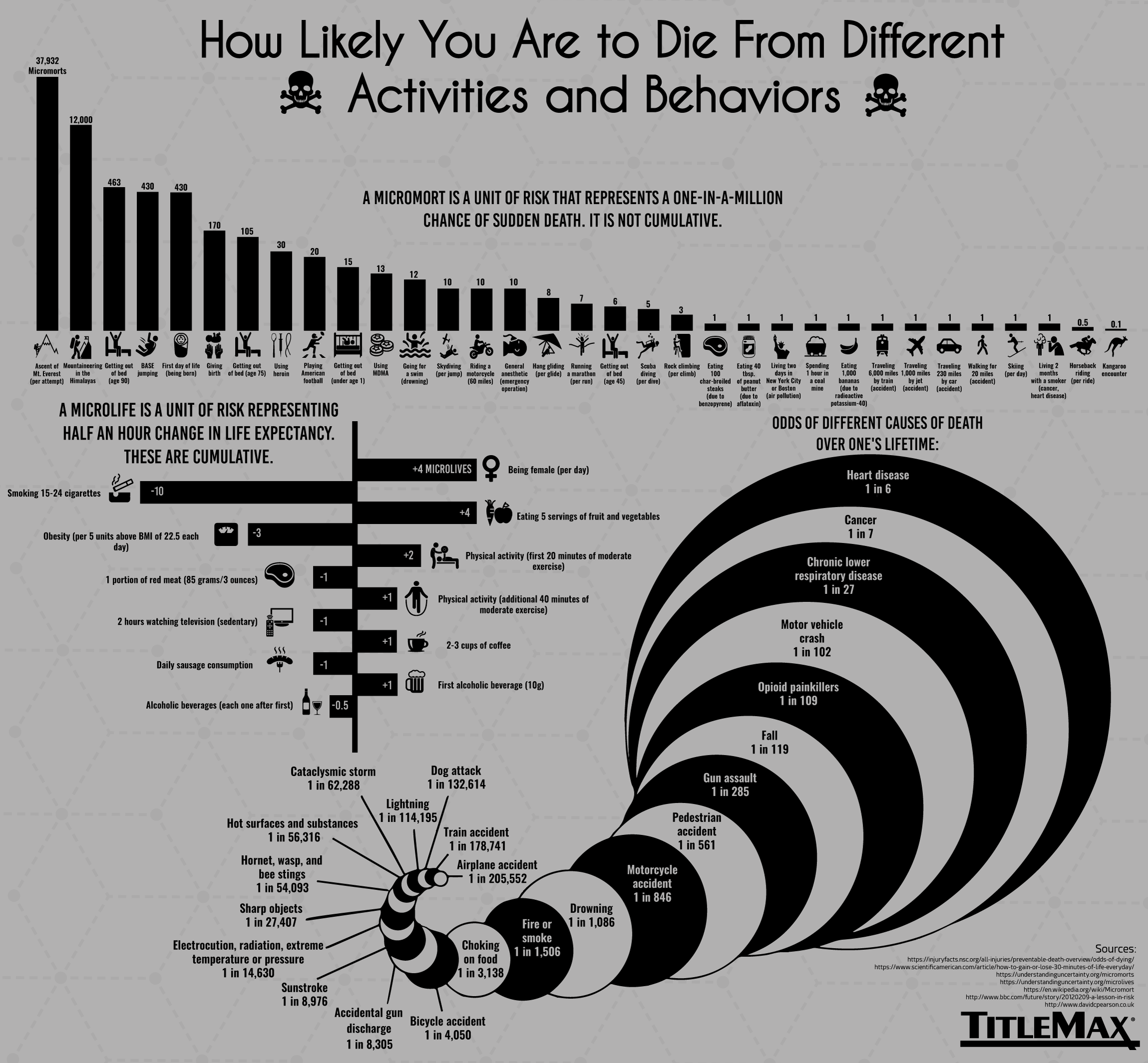



How Likely You Are To Die From Different Activities And Behaviors Infographic Article
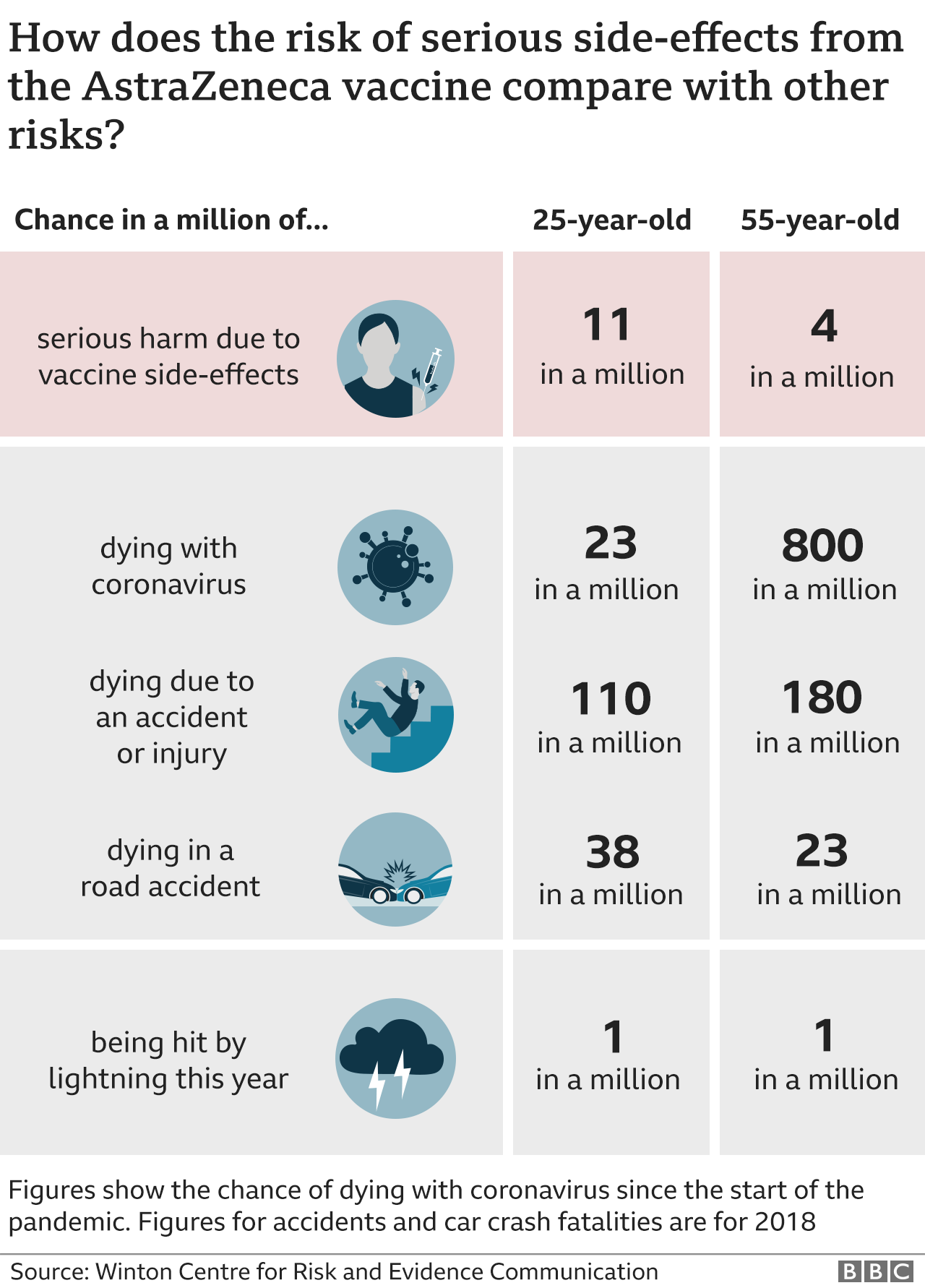



Astrazeneca Vaccine How Do You Weigh Up The Risks And Benefits c News




What Are The Odds The Annals Of Thoracic Surgery




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Risk Differences And Rate Differences




Risk Estimates Relative Risk Ratio And Odds Ratio Analyses For Download Table



Confidence Intervals And P Values




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube




Power Calculations For Gwass The Smallest Odds Ratio Case Control Download Scientific Diagram




What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora




Solved Drawn From Lecture Week 11 Day 1 23 3 Day Care C Chegg Com




Cecile Janssens A Reminder That Odds Ratios Massively Overestimate Relative Risks When Outcome Is Common In The Population Or By Study Design E G Case Control Studies Io Is Proportion Of Cases




Odds Ratio For The Risk Of Having A Prescription Pre Versus Download Table




Single Workplace Factor Odds Ratios Between High Risk Versus Low Risk Download Table




Relative Risk Wikipedia
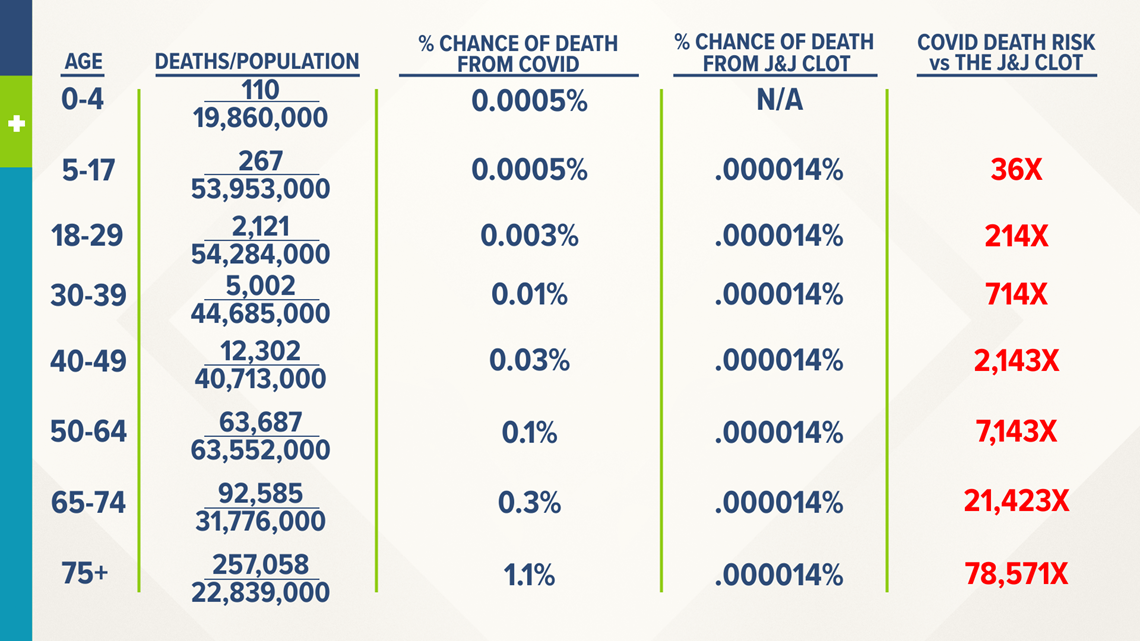



The Odds Of Dying From A J J Vaccine Related Blood Clot Vs Dying From Covid 19 Newscentermaine Com




Risk Ratio Versus Odds Ratio Dr Journal Club




Hsrp 734 Advanced Statistical Methods June 5 Ppt Video Online Download



Clinical Epidemiology Bootcamp




Statquest Odds Ratios And Log Odds Ratios Clearly Explained Youtube



No comments:
Post a Comment